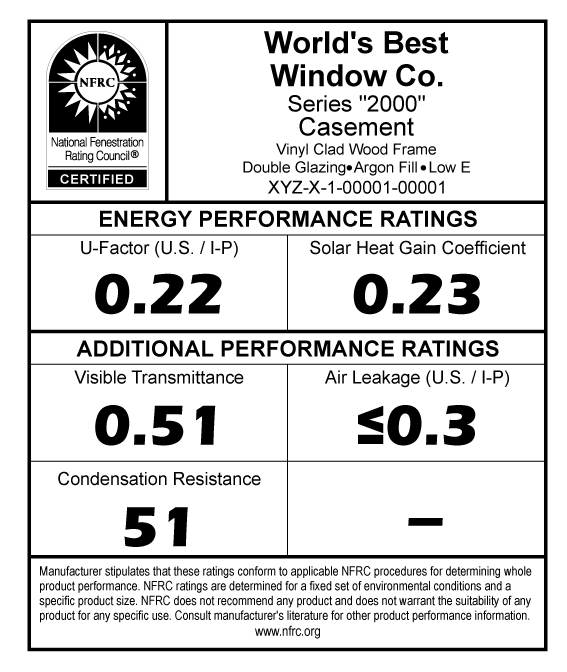
When it comes to selecting new windows and doors for your home, energy efficiency is often a top priority. The National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) label plays a crucial role in helping homeowners make informed decisions. This comprehensive guide will decode the NFRC label, explaining its components and how they impact your home’s energy performance and comfort.
What is the NFRC?
The NFRC is an independent, non-profit organization that provides accurate information on the energy performance of windows, doors, and skylights. By standardizing the way energy efficiency is measured, the NFRC label offers a reliable method for comparing different products, regardless of brand or manufacturer.
Understanding the NFRC Label
The NFRC label includes several key metrics that measure a product’s energy performance. Here’s what each section means for your home:
1. U-Factor
- Definition: The U-Factor measures how well a window or door prevents heat from escaping a home. It is expressed in numbers ranging from 0.20 to 1.20. The lower the U-Factor, the better the product is at keeping heat inside.
- Impact on Your Home: A lower U-Factor is particularly beneficial in colder climates, where retaining interior heat is crucial for comfort and energy savings.
2. Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC)
- Definition: SHGC measures how much solar radiation a window or door allows into your home, expressed as a number between 0 and 1. A lower SHGC means less solar heat is transmitted.
- Impact on Your Home: In hot climates, a lower SHGC can reduce cooling needs by blocking excessive solar heat, while in colder areas, a higher SHGC can provide passive solar heating.
3. Visible Transmittance (VT)
- Definition: VT indicates how much natural light passes through a window or door. It’s measured on a scale from 0 to 1, with higher values indicating more light transmission.
- Impact on Your Home: High VT values enhance daylighting, reducing the need for artificial lighting and creating a brighter, more inviting indoor environment.
4. Air Leakage (AL)
- Definition: This metric measures the rate at which air passes through joints in the window or door, with lower values indicating less air leakage.
- Impact on Your Home: Reducing air leakage is essential for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures and lowering energy costs.
5. Condensation Resistance
- Definition: This rating measures how well a window or door resists the formation of condensation on the interior surface. It is scored from 0 to 100, with higher numbers indicating better resistance.
- Impact on Your Home: Effective condensation resistance helps prevent mold growth and water damage, contributing to a healthier indoor environment.
The Benefits of Choosing NFRC-Labeled Products
Selecting windows and doors with NFRC labels ensures you’re choosing energy-efficient products that can lead to significant savings on heating and cooling bills. Additionally, these products can enhance indoor comfort, reduce environmental impact, and potentially increase your home’s value.
How to Use NFRC Labels in Your Selection Process
When shopping for windows and doors, compare the NFRC labels of different products to find the best fit for your climate and home’s design. Consider the specific needs of each room and how different ratings can impact overall comfort and energy efficiency.
Conclusion
The NFRC label is an invaluable tool for homeowners looking to upgrade their windows and doors. By understanding and utilizing the information it provides, you can make choices that enhance your home’s energy performance, comfort, and sustainability. Remember, the right windows and doors can transform your living space, making it more comfortable, energy-efficient, and enjoyable for years to come.